Release Management
Release Management is the process of coordinating and communicating the release of changes to a service. Release Management is a Service Transition process, so this flow separates the Development and Operations activities, as well as the tasks transitioning the service from Development to Operations.
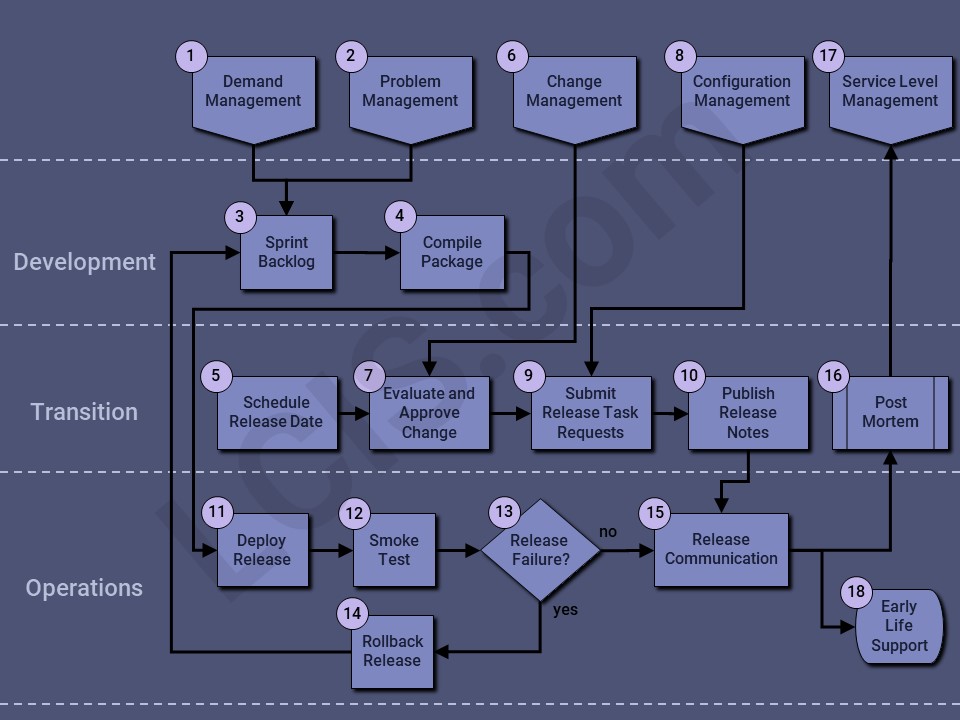
- Demand Management allows prioritization of new services, regulatory changes, and enhancement requests.
- Problem Management may identify service defects requiring code changes.
- In an Agile environment, defects and enhancements prioritized by Demand Management (1) and Problem Management (2) are added to the Sprint Backlog for analysis, coding and testing.
- The build package is compiled and delivered to the Operations team for deployment.
The following steps 5 – 10 occur in parallel with steps 3 – 4: - A release date is scheduled in accordance with agreed-upon maintenance windows and outside of any company-mandated freeze periods. Exceptions to these rules may be allowed for Emergency Changes.
- A Change Management record is created for the scheduled release date.
- The Change is evaluated to ensure compliance with company release standards, including testing results, and back-out plan.
- Configuration Management is leveraged to identify resources required to implement the release, and services impacted by the changes.
- Tasks required for a successful release are created and assigned to the resources charged with executing the tasks. For example, a DBA resource may need to be scheduled to manually stop the database service prior to the release, and start it again following the completion.
- Release notes are published with detail of the items being released from the Sprint Backlog.
- Release is deployed in production per scheduled release tasks (9).
- A smoke test is performed to confirm basic functions of the service were not impacted by the release.
- If the smoke test is unsuccessful, the release has failed. A release failure may also be identified by Availability Management and/or Incident Management.
- If the release fails, the rollback process is initiated, and the release items go back on the Sprint Backlog (3).
- If the release is successful, a communication is sent to stakeholders with the release notes (10).
- A Post Mortem meeting is held with the transition team to identify successes, failures, and follow up tasks.
- Service Level Management is updated with any changes prescribed by the release.
- For major releases, Early Life Support is initiated to monitor the service for a short period of time to ensure the release had no unintended consequences.