Configuration Management
Configuration Management is at the center of ITSM. The Configuration Item (CI) is the common key linking all the ITSM processes and functions. A CI can be anything from a hardware device to a process document, but for the purposes of this example, the CI is a software application. In ITSM, we’re concerned with “servicing” this software application, not just programming the code, so we refer to it as a “service” not “software”.
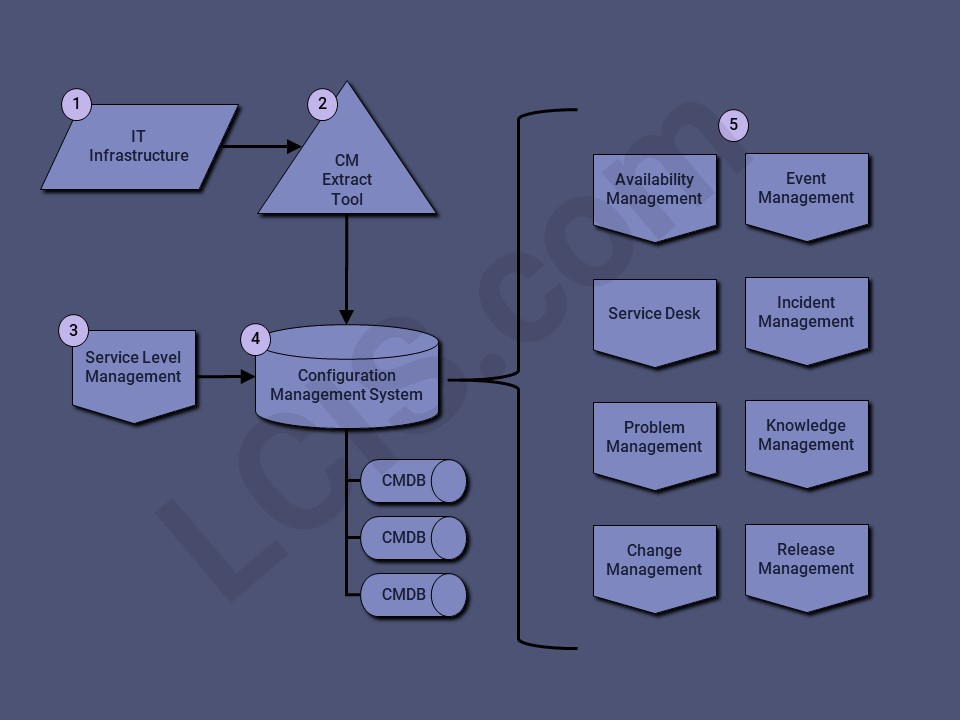
- The IT Infrastructure includes hardware, network, and services running on the hardware.
- Configuration Management can be populated with CIs automatically by scanning tools that extract the IT infrastructure configuration data like software licenses and DNS records.
- Service Level Management defines the CIs created during the Service Design stage, including the service itself, as well as components (like virtual server, cluster, database server, web server, etc.).
- The Configuration Management System (CMS) can be a single or series of Configuration Management Databases (CMDBs).
- The CMDB stores the CI data in a format that can be linked to all the Service Management processes and functions, allowing for awareness of key dependencies required for successful operation of the service: